“Football Tactics Popular in Spain
Related Articles Football Tactics Popular in Spain
Football Tactics Popular in Spain
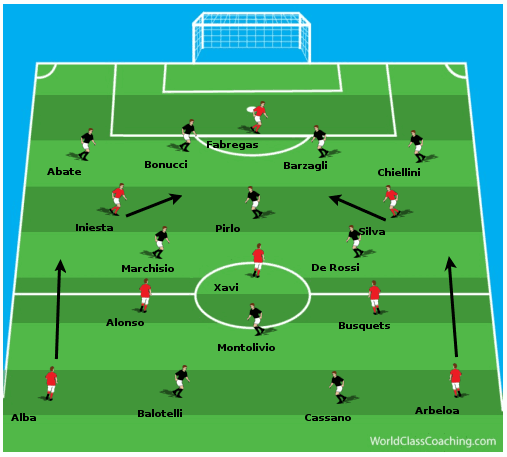
Spanish football has long been celebrated for its tactical innovation and distinctive style of play. From the dominance of "tiki-taka" to the recent rise of high-pressing systems, Spanish coaches and teams have consistently pushed the boundaries of footballing strategy. This article explores some of the most popular and influential football tactics in Spain, examining their key principles, historical context, and notable examples.
1. Tiki-Taka: The Art of Possession
Perhaps the most iconic tactical system associated with Spanish football is "tiki-taka." Popularized by FC Barcelona under the management of Pep Guardiola, tiki-taka is a style of play based on short, precise passing, constant movement, and maintaining possession of the ball. The primary goal of tiki-taka is to control the game by dominating possession, tiring out opponents, and creating opportunities to score through patient build-up play.
Key principles of tiki-taka include:
- Short Passing: Players prioritize short, simple passes to maintain possession and circulate the ball.
- Constant Movement: Players are constantly moving and interchanging positions to create passing lanes and disrupt the opposition’s defensive structure.
- Positional Play: Players adhere to specific positional roles and responsibilities, ensuring that the team maintains a balanced shape and avoids being caught out of position.
- Pressing: When possession is lost, players immediately press the opposition to win the ball back quickly.
Tiki-taka reached its peak with Guardiola’s Barcelona team from 2008 to 2012, which featured legendary players such as Lionel Messi, Xavi Hernandez, and Andres Iniesta. Barcelona’s tiki-taka style was also adopted by the Spanish national team, which won the 2010 FIFA World Cup and the 2008 and 2012 European Championships.
While tiki-taka has been criticized for being overly cautious and lacking directness, its emphasis on possession and control has had a lasting impact on Spanish football. Many teams in Spain still incorporate elements of tiki-taka into their style of play, even if they do not adhere to it strictly.
2. Juego de Posición: Positional Play
"Juego de Posición," which translates to "positional play," is a tactical approach that emphasizes the importance of occupying specific zones on the field to create passing lanes, maintain balance, and control the game. Juego de Posición is closely related to tiki-taka, but it places a greater emphasis on the strategic positioning of players rather than simply passing the ball for the sake of possession.
Key principles of Juego de Posición include:

- Occupation of Zones: Players are assigned specific zones on the field to occupy, ensuring that the team maintains a balanced shape and creates passing options.
- Third Man Runs: Players make diagonal runs to create passing lanes and disrupt the opposition’s defensive structure.
- Numerical Superiority: Players create numerical advantages in specific areas of the field to facilitate ball progression and create scoring opportunities.
- Patience and Circulation: Players patiently circulate the ball, waiting for the right moment to penetrate the opposition’s defense.
Juego de Posición has been implemented by several successful coaches in Spanish football, including Pep Guardiola, Johan Cruyff, and Juanma Lillo. These coaches believe that by controlling space and creating numerical advantages, teams can dictate the tempo of the game and create high-quality scoring opportunities.
3. High Pressing: Winning the Ball Back High Up the Pitch
In recent years, high pressing has become an increasingly popular tactic in Spanish football. High pressing involves pressing the opposition high up the pitch, often in their own half, to win the ball back quickly and create scoring opportunities. The goal of high pressing is to disrupt the opposition’s build-up play, force them into mistakes, and create turnovers in dangerous areas.
Key principles of high pressing include:
- Aggressive Pressing: Players aggressively press the opposition when they have the ball, closing down space and forcing them to make quick decisions.
- Coordination and Timing: Players must coordinate their pressing efforts, ensuring that they move as a unit and close down passing lanes effectively.
- Intensity and Stamina: High pressing requires a high level of intensity and stamina, as players must constantly run and exert themselves to win the ball back.
- Compactness: Players must maintain a compact shape, reducing the space available for the opposition to play through.
High pressing has been implemented by several successful teams in Spanish football, including Atletico Madrid under Diego Simeone and Real Sociedad under Imanol Alguacil. These teams have used high pressing to disrupt the opposition’s rhythm, force turnovers, and create scoring opportunities.
4. Counter-Attacking: Exploiting the Opposition’s Weaknesses
Counter-attacking is a tactical approach that focuses on quickly transitioning from defense to attack, exploiting the opposition’s weaknesses when they are out of position. Counter-attacking teams typically defend in a compact shape, absorb pressure, and then launch quick attacks when they win the ball back.
Key principles of counter-attacking include:
- Compact Defense: Players defend in a compact shape, reducing the space available for the opposition to play through.
- Quick Transitions: Players quickly transition from defense to attack, exploiting the opposition’s defensive vulnerabilities.
- Pace and Directness: Players use pace and directness to quickly move the ball forward, creating scoring opportunities.
- Clinical Finishing: Players must be clinical in front of goal, converting counter-attacking opportunities into goals.
Counter-attacking has been implemented by several successful teams in Spanish football, including Real Madrid under Jose Mourinho and Valencia under Marcelino Garcia Toral. These teams have used counter-attacking to exploit the opposition’s weaknesses, score goals, and win matches.
5. Defending in a Low Block: Defensive Solidity
Defending in a low block is a tactical approach that focuses on maintaining a compact defensive shape deep in one’s own half, making it difficult for the opposition to penetrate. Teams that defend in a low block typically prioritize defensive solidity and organization, aiming to frustrate the opposition and limit their scoring opportunities.
Key principles of defending in a low block include:
- Compact Shape: Players maintain a compact shape, reducing the space available for the opposition to play through.
- Discipline and Organization: Players must be disciplined and organized, adhering to their defensive responsibilities and maintaining their shape.
- Patience and Resilience: Players must be patient and resilient, willing to absorb pressure and wait for opportunities to counter-attack.
- Clearances and Interceptions: Players must be effective at clearing the ball and intercepting passes, preventing the opposition from creating scoring opportunities.
Defending in a low block has been implemented by several teams in Spanish football, particularly those with limited resources or those facing stronger opponents. While it may not be the most aesthetically pleasing style of play, defending in a low block can be an effective way to frustrate the opposition and secure valuable points.
6. The 4-3-3 Formation: A Versatile System
The 4-3-3 formation is a versatile system that has been widely used in Spanish football for many years. The 4-3-3 typically consists of four defenders, three midfielders, and three forwards. This formation provides a good balance between attack and defense, allowing teams to control possession, create scoring opportunities, and defend effectively.
Key features of the 4-3-3 formation include:
- Width in Attack: The three forwards provide width in attack, stretching the opposition’s defense and creating space for midfielders to run into.
- Midfield Control: The three midfielders control possession and dictate the tempo of the game.
- Defensive Solidity: The four defenders provide defensive solidity, protecting the goal and preventing the opposition from creating scoring opportunities.
- Flexibility: The 4-3-3 formation can be easily adapted to suit different game situations, allowing teams to switch between attacking and defensive strategies.
The 4-3-3 formation has been used by many successful teams in Spanish football, including FC Barcelona, Real Madrid, and Valencia. Its versatility and balance make it a popular choice for coaches looking to implement a well-rounded tactical system.
Conclusion
Spanish football has a rich tactical history, with a diverse range of styles and approaches. From the iconic tiki-taka to the recent rise of high-pressing systems, Spanish coaches and teams have consistently pushed the boundaries of footballing strategy. The tactics discussed in this article represent some of the most popular and influential in Spanish football, reflecting the country’s commitment to innovation, creativity, and tactical excellence. As football continues to evolve, it is likely that Spanish coaches and teams will continue to be at the forefront of tactical innovation, shaping the future of the game.

r8xspp